Understanding User Experience (UX) in Web Design
In today’s digital age, the importance of user experience (UX) in web design cannot be overstated. As websites and applications become more intricate, the user’s experience plays a pivotal role in determining the success of a digital product. This article delves deep into the Understanding of User Experience (UX) in Web Design, exploring its significance, various facets, and its undeniable impact on web design.
Key Takeaways:
- UX design is a holistic approach that focuses on the end-to-end experience of users.
- A good UX design ensures that a product is not just usable, but also delightful and efficient.
- The difference between UX and UI is crucial; while they often overlap, they cater to different aspects of the design process.
- Investing in UX design can lead to better user satisfaction and can be a determining factor in a product’s success.
What is User Experience (UX) Design?

User experience (UX) design is the process design teams employ to create products that offer meaningful and relevant experiences to users. This involves the entire journey of acquiring and integrating the product, including aspects of branding, design, usability, and function. UX design is not just about making a product usable; it’s about making it useful, efficient, and enjoyable. The ultimate goal is to design solutions that address user pain points and needs. After all, a product that doesn’t serve a purpose will find no takers.
“No product is an island. A product is more than the product. It is a cohesive, integrated set of experiences. Think through all of the stages of a product or service – from initial intentions through final reflections, from the first usage to help, service, and maintenance. Make them all work together seamlessly.” – Don Norman, inventor of the term “User Experience.”
UX vs UI: What’s the Difference?
Often, the terms “User Experience Design” and “User Interface Design” are used interchangeably. However, while there’s some overlap, they are distinct disciplines. UI focuses on the look and feel of a product, the presentation, and the interactivity. It’s about ensuring that the interface is visually appealing, coherent, and in line with design guidelines and best practices.
On the other hand, UX is a broader field that encompasses UI and focuses on the overall feel of the experience. It ensures that the product logically flows from one step to the next, offering a seamless and intuitive user journey.
For a clearer understanding, consider this analogy: If a product was a human body, then the bones represent the code that gives it structure. The organs, representing the UI, determine how it looks and presents itself, while the UX is the feeling one gets when interacting with it.
The Importance of Good User Experience
A product that offers a good user experience meets the specific needs of its users. It’s not just about creating a usable product, but about other aspects of the experience, such as pleasure, efficiency, and fun. The aim is to design products that users can form meaningful experiences with. For instance, when using a digital product, factors like intuitive navigation, clear cues guiding users, and timely visibility of essential aspects play a crucial role in determining the UX.
UX Design Salary and Career Prospects
UX design has emerged as a lucrative and fulfilling career option. As businesses recognize the importance of offering a stellar user experience, the demand for skilled UX designers has skyrocketed. On average, a UX designer earns significantly more than a graphic designer. This can be attributed to the multidisciplinary nature of UX design, which requires professionals to possess a diverse skill set, including research, design, testing, and more.
Incorporating UX Design in Web Design
Web design is not just about creating visually appealing websites. It’s about offering a seamless and intuitive user journey. Here are some ways to incorporate UX design principles into web design:
- User-Centered Design: This approach places the user at the center of the design process. It involves understanding user needs, preferences, and behaviors and then designing the website accordingly.
- Consistent Navigation: Ensure that the website navigation is consistent across all pages. This offers a sense of familiarity to users and makes the browsing experience smoother.
- Mobile Responsiveness: With a significant number of users accessing websites from mobile devices, it’s crucial to ensure that the website is mobile-responsive.
Factors Influencing User Experience
User experience (UX) is not just about the design or the interface of a product. It delves deeper into understanding the users, their needs, values, abilities, and also their limitations. Several factors influence the UX, and understanding these can help designers create more user-centric products.
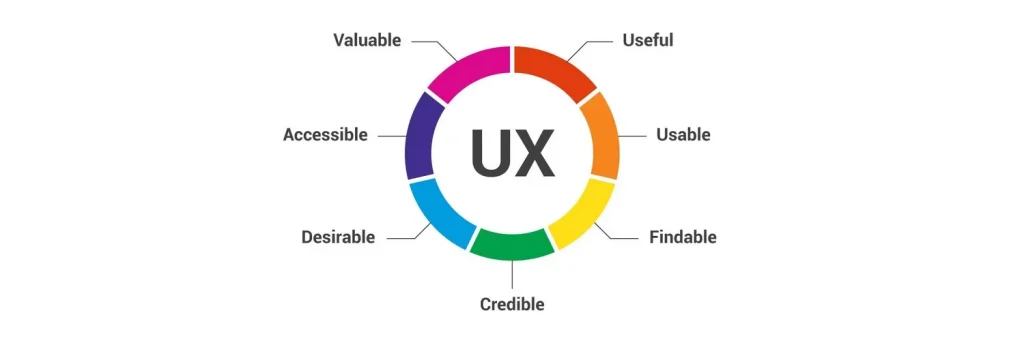
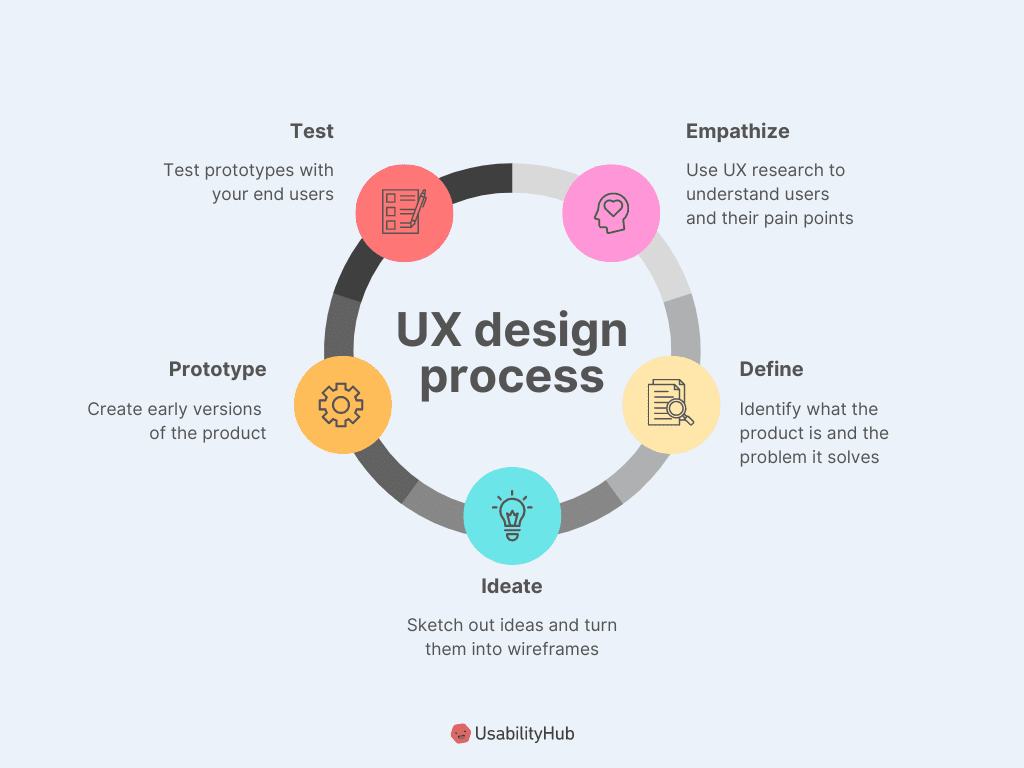
Core Elements of UX
Peter Morville, a renowned UX expert, represents the core elements of UX through his User Experience Honeycomb. He emphasizes that for a user experience to be meaningful and valuable, the following factors must be considered:
- Useful: The content should be original and fulfill a specific need.
- Usable: The site or product must be easy to use.
- Desirable: Elements like image, identity, brand, and design should evoke emotion and appreciation.
- Findable: Users should easily navigate and locate content both on and off the site.
- Accessible: The content should be accessible to people with disabilities.
- Credible: Users must trust the information provided to them.
Disciplines Encompassing User Experience
UX is a vast field that encompasses various disciplines. Some of these include:
- Project Management: This involves planning, organizing, and managing resources for a project.
- User Research: This focuses on understanding user behaviors, needs, and motivations.
- Usability Evaluation: This assesses how easily users can learn and use a product.
- Information Architecture (IA): This deals with organizing, structuring, and presenting information to users.
- User Interface Design: This anticipates user needs and ensures the interface facilitates those actions.
- Interaction Design (IxD): This creates engaging interactive systems.
- Visual Design: This ensures the interface is aesthetically pleasing.
- Content Strategy: This involves planning, creating, delivering, and governing content.
- Accessibility: This ensures disabled individuals can access or benefit from a site or application.
For more insights into the core elements of UX, you can refer to the User Experience Honeycomb diagram by Peter Morville.
UX Design Examples in Web Design
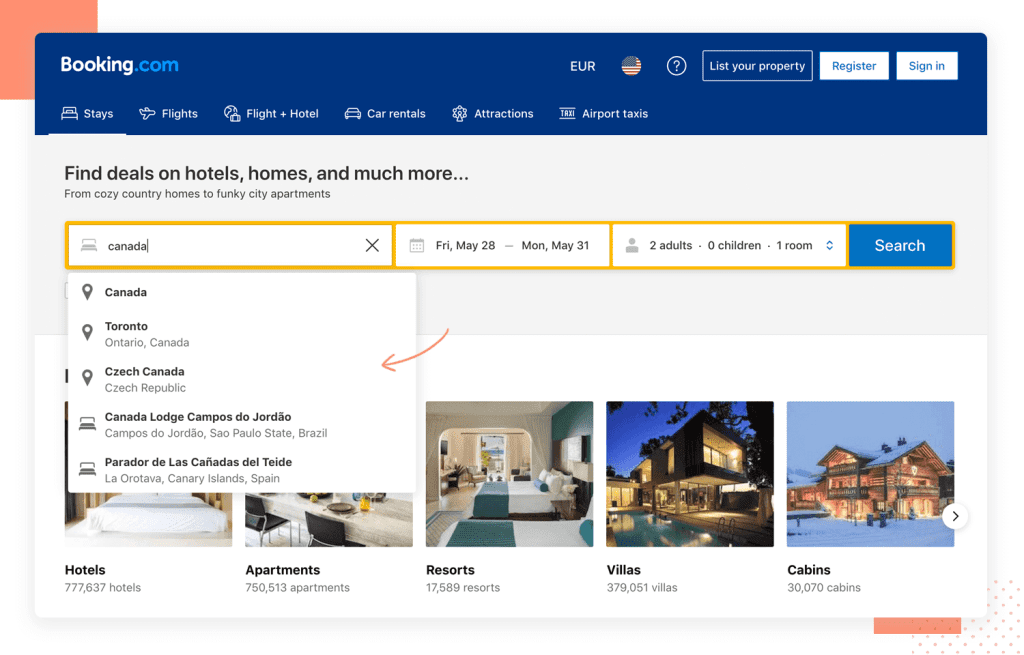
When it comes to web design, UX plays a pivotal role in determining the success of a website. Here are some examples of how UX design principles are incorporated into web design:
- Responsive Design: With the increasing use of mobile devices, it’s essential for websites to be mobile-responsive. This ensures that users have a seamless experience, irrespective of the device they use.
- Clear Call-to-Action (CTA) Buttons: CTAs guide users towards the desired action, be it signing up, purchasing, or downloading. Clear and compelling CTAs can significantly improve conversion rates.
- Intuitive Navigation: A well-structured navigation menu ensures that users can easily find what they’re looking for, enhancing the overall user experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about UX in Web Design
What is User Experience (UX)?
User Experience (UX) refers to the overall experience a user has when interacting with a product, system, or service. It encompasses a wide range of factors, including usability, accessibility, performance, design/aesthetics, utility, ergonomics, overall human interaction, and marketing.
How is UX different from UI?
While UX focuses on the overall feel and experience of using a product, User Interface (UI) is about the specific assets users interact with. This includes buttons, icons, spacing, and responsive design elements. In essence, UI is a crucial component of UX but focuses more on the visual aspects of design.
Why is UX design important?
UX design is essential because it aims to fulfill user needs, ensuring the overall experience is smooth, intuitive, and user-friendly. A good UX can lead to increased user satisfaction, loyalty, and potentially higher revenue for businesses.
What are some common tools used in UX design?
Some popular tools include Sketch, Figma, Adobe XD, InVision, and Axure. These tools help designers create wireframes, prototypes, and high-fidelity designs.
How can I get started with UX design?
Begin by understanding the principles of design, user behavior, and psychology. Online courses, workshops, and reading materials can provide foundational knowledge. Building a portfolio by working on real-world projects, even if they’re personal or pro bono, can also be beneficial.
What’s the difference between a UX designer and a web designer?
A UX designer focuses on the overall feel of the product, ensuring it’s user-friendly, intuitive, and meets the needs of the user. A web designer, on the other hand, focuses on the aesthetic aspects of the website and its overall look and feel.





![The Impact of Having a Business Website: A Survey Conducted by New Perspective Design in South Africa [Case Study 2025]](https://www.newperspectivestudio.co.za/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/The-Impact-of-Having-a-Business-Website-survey.jpg)